Melatonin - hormone secreted by the pineal gland at night
Keywords: Anti-inflammatory agent, Antioxidant, Melatonin, Melatonin receptors
Melatonin (MLT) is an indoleamine hormone secreted by the pineal gland at night and has an essential role in regulating human circadian rhythms (the internal 24-h clock) and sleep-wake patterns. However, it has recently gained considerable attention for its demonstrated ability in disease management.
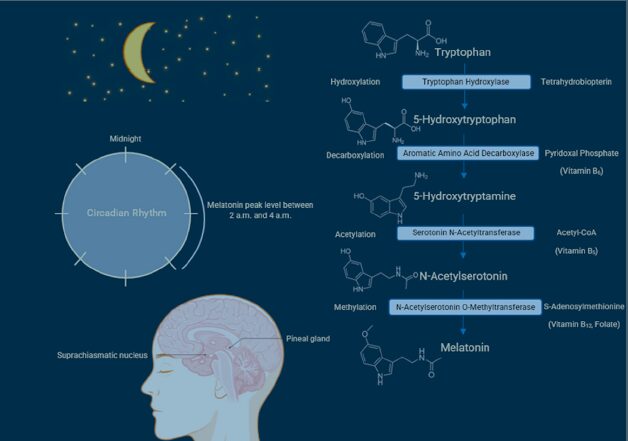
Fig. 1. Melatonin synthesis and secretion in the pineal gland. (Note: This figure is self-designed by the authors using Biorender® software).
Initially, several studies demonstrated that exogenous MLT effectively improved sleep, most likely because of its chronobiotic properties, and it has been shown to contribute to adjusting and maintaining a regular circadian rhythm. However, there are many other health effects associated with the application of MLT: MLT supplementation, for example, is beneficial for inflammation markers, hypertension, oxidative stress, and metabolic syndrome [3]. In addition to being available over-the-counter, MLT can also be obtained via medical prescription. In contrast, drugs used to treat conditions such as chronic inflammation may have undesirable side effects, while nutraceuticals such as MLT are known to be beneficial in treating inflammation due to their high safety and tolerability.
Review article: review of melatonin as a promising nutritional and nutraceutical supplement. Waad W. Kamfar a,b, Husam M. Khraiwesh m, Mohammed O. Ibrahim c, Alaa. H. Qadhi a, Wedad F. Azhar a, Khloud J. Ghafouri a, Maha H. Alhussain d, Abdullah. F. Aldairi e, Abdullah M. AlShahrani f, Abdullah F. Alghannam g, Rwaa H. Abdulal h,i, Abed H. Al-Slaihat j, Maysoun S. Qutob k, Mahmoud E. Elrggal l, Mazen M. Ghaith e, Firas S. Azzeh a.*